What is the best fuel to power steam boilers?
Posted 30th July 2024
What is the best fuel to power industrial boilers?
Industrial boilers are at the heart of many manufacturing processes, providing essential steam and hot water for everything from food production to chemical refining, but what fuel is the best for powering your boiler?
There is no one-size-fits-all answer, as the choice of fuel depends on several important factors such as cost, environmental impact, and the size and requirements of your process. Each fuel has its advantages and considerations which is what will be explored in this blog, helping you to understand the most applicable option for your current or future projects.
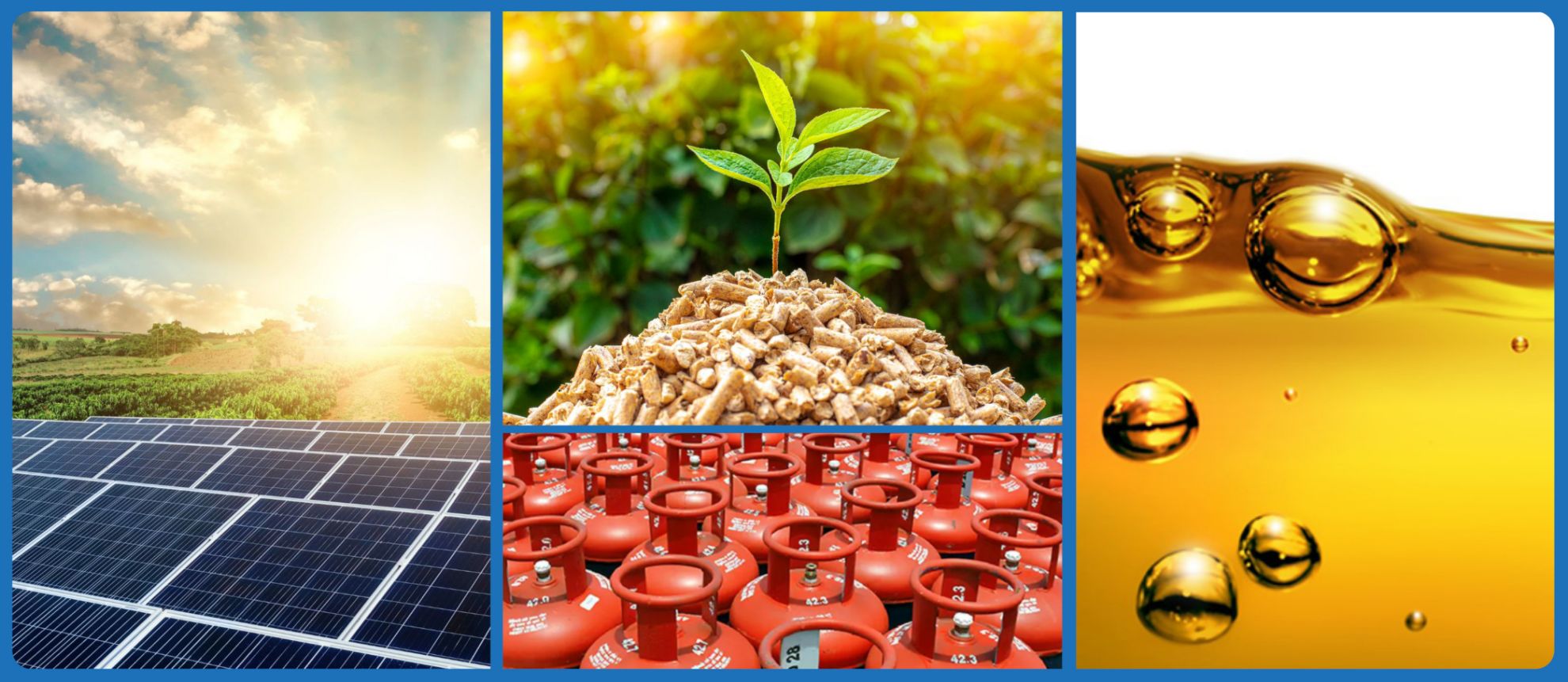
All fuels belong to one of two core categories. Fossil fuels, such as oil and gas, and renewable fuels like biomass and electricity. While organisations across the globe continue to search for more ways to reduce their carbon footprint, moving to a renewable fuel source is still out of reach for some despite their good intentions.
Fossil Fuels
Fossil fuels are a reliable and familiar choice still widely used across the industry. They are readily available and convenient to use, making them the go-to option for many organisations.
Natural Gas
Natural gas remains the most popular choices for many industrial applications for several reasons. It’s clean burning, and highly energy efficient. However, it does require a natural gas supply which is not available in some remote locations. Additionally, gas prices can fluctuate dramatically especially when demand is high.
LPG Gas
LPG (Liquefied Petroleum Gas) is another popular choice for fuelling industrial boilers. LPG typically achieves higher combustion efficiency due to its higher calorific value and cleaner burning properties, making it a slightly cleaner option to natural gas. However, LPG is also generally more expensive per unit of energy than natural gas, though this can vary depending on market conditions and location.
Unlike natural gas, LPG is not transported via mains pipework. It is required to be stored in pressurised tanks or canisters. These must be stored outside the facility and conform to numerous rules and regulations for safety reasons. However due to the storage and transportation methods, it can be used in remote areas with no mains (natural) gas supply.
Oil
Both light and heavy oil can be used to fuel industrial boilers, although due to the high emissions generated, heavy oil is rarely used within the UK anymore.
Light oil is a popular fuel choice due to its excellent availability across regions and it’s energy dense so can provide a higher heat output per unit of fuel than other options. The significant disadvantage of oil is that even light oil produces significantly higher emissions than LPG and natural gas.
Renewable Fuels
Biomass
Biomass is an eco-friendly option using organic materials such as wood chips, pellets, and agricultural byproducts.
Although this may sound like the ideal sustainable fuel solution, it is vital users take into consideration the volume of product needed to achieve the same output as oil and gas, and the environmental impact of transporting and burning such volumes.
Users also need to consider storage space and conditions, as biomass fuels are susceptible to variable moisture content which can significantly affect combustion efficiency. The volume and storage required for biomass fuelling could drastically increase the overall cost associated with burning biomass, thus outweighing the advantage of it being eco-friendly.
Electricity
Electric energy or electric fuel is one of the most widely discussed topics of recent years. With electric cars continuing to grow in popularity is the electric boiler going to go the same way?
Let’s looks at the details.
Unlike traditional boilers, electric boilers don’t involve combustion. They use electricity to generate heat offering a clean and alternative to traditional fuels with lower emissions. However due to the amount of electricity required for many industrial applications, these are unlikely to be a cost effective option for large scale use.
So while an electric boiler may be the most environmentally friendly option, with the current infrastructure and cost implications, they are not financially viable for many organisations.
Hydrogen
Hydrogen has become a buzz word in recent years when discussing the topic of industrial fuel choices. Although often considered a renewable energy source, Hydrogen is only renewable if the method used in its extraction is also renewable. Green hydrogen is produced using renewable electricity from solar panels or wind turbines, however Grey hydrogen is produced from fossil fuels so is consequently not renewable. There are other grades of hydrogen including blue, pink and yellow, however for the purpose of this article we will be looking at Green Hydrogen specifically.
Green Hydrogen combustion in boilers produces water vapor as the only emission, making it an attractive option for reducing a processes greenhouse gas emissions. Yet, despite it’s green and clean reputation, there are a number of disadvantages to using hydrogen that need to be considered.
Hydrogen has a low volumetric energy density, requiring high-pressure tanks, temperature regulation, and chemical carriers for storage and transportation. Also, the production, storage, and distribution infrastructure for hydrogen is currently more expensive than conventional fuels.
So, while Hydrogen holds great potential as a clean fuel for industrial applications, the technology and infrastructure need to evolve for hydrogen to play a significant role in a sustainable energy future.
Choosing the Right Fuel
To understand the best fuel for your application you need to consider the following points thoroughly.
· Cost - Both initial fuel cost and price fluctuations need to be considered.
· Efficiency - Different fuels offer varying heat output per unit, impacting operational costs.
· Regulations - Environmental regulations might limit the use of fuels with high emissions.
· Application - The specific industry and its heating needs play a significant role.
The Verdict
The best fuel for your industrial boiler is the one that fits your demand, is accessible, and is financially sustainable long term. Your heart might tell you to go for a renewable fuel, but if your pockets aren’t deep enough you may cause yourself and your organisation more problems long term.
The good news? You can contact us on 01535 665225 if you need advice on fuel options and the fuel consumption of our boilers.
Read more of our news and blog content using the links below.
Enjoyed this article?
Read our blog about upgrading your boiler to improve efficiency.